Concepts Overview
Several key concepts form the foundation of creating and working with knowledge graphs in whyhow. Understanding these concepts is crucial for effectively leveraging the platform's capabilities. This overview provides a high-level introduction to the main concepts in whyhow.
Workspace
A workspace is a virtual environment within whyhow where you can organize and manage your documents, schemas, and knowledge graphs. It serves as a container for all the resources related to a specific project or domain.
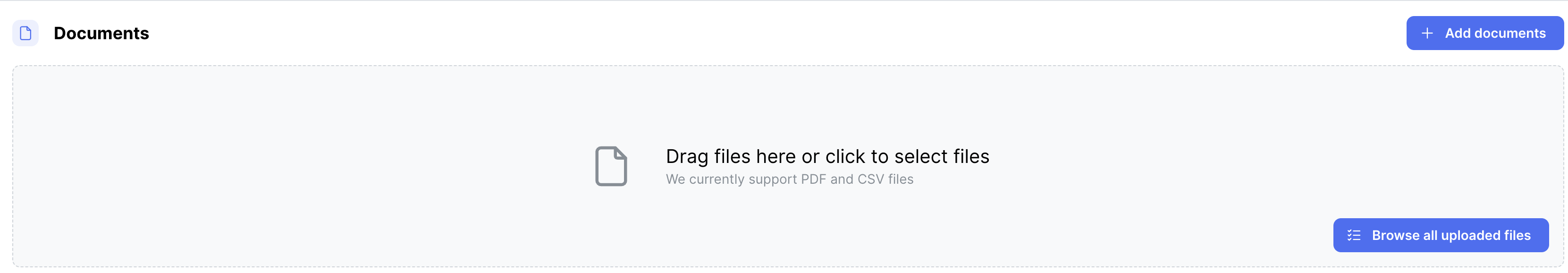
Document
Documents are the source of data for creating knowledge graphs in whyhow. They can be structured (e.g., CSV files, JSON files) or unstructured (e.g., PDF files, TXT files) and contain the information that will be extracted and transformed into graph nodes and relationships.
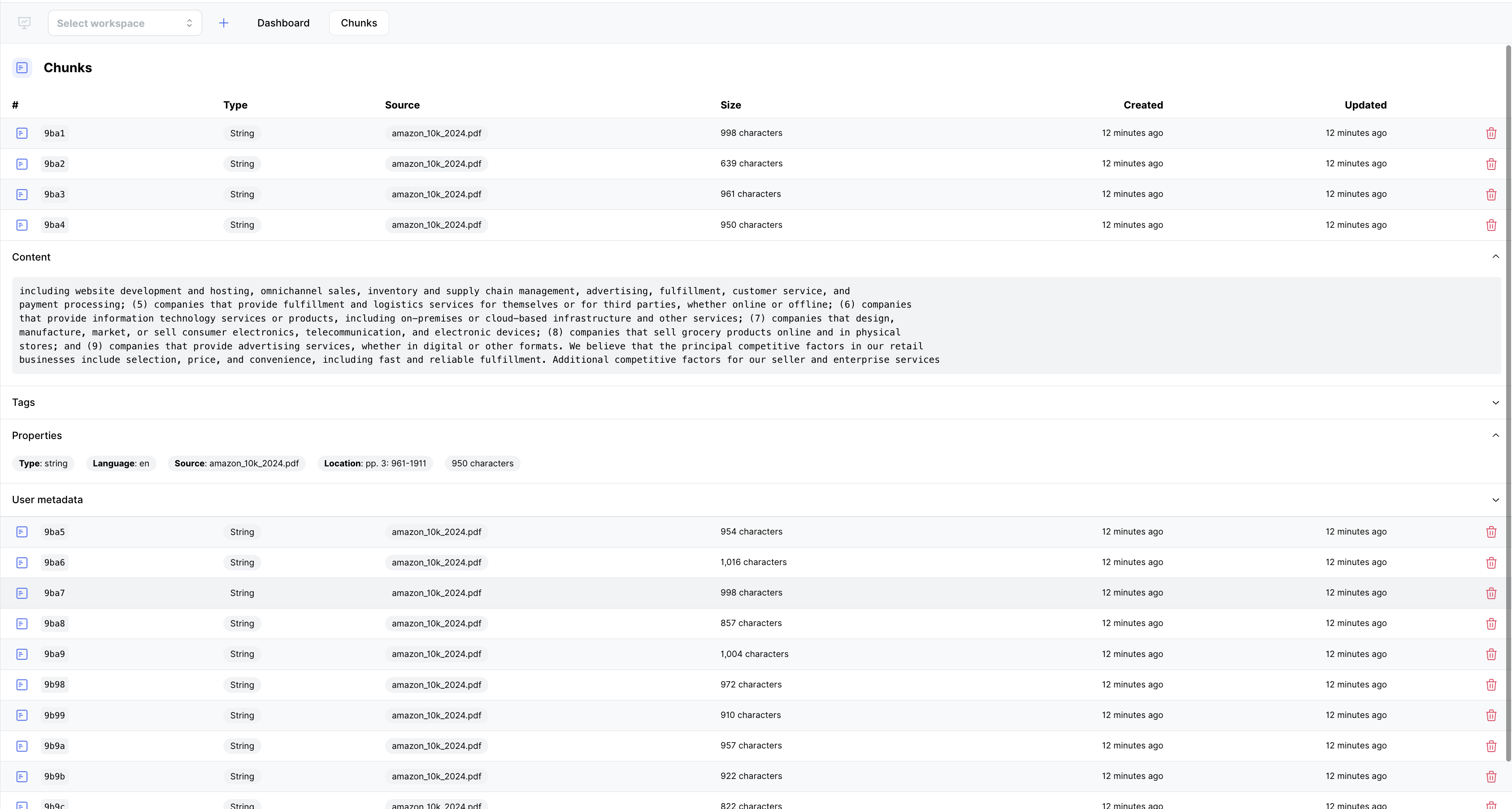
Chunk
Chunks are minor data extracted from documents during the document processing phase. For structured data, each row in a CSV file represents a chunk. The platform splits the document into meaningful chunks based on paragraphs or sections for unstructured data.
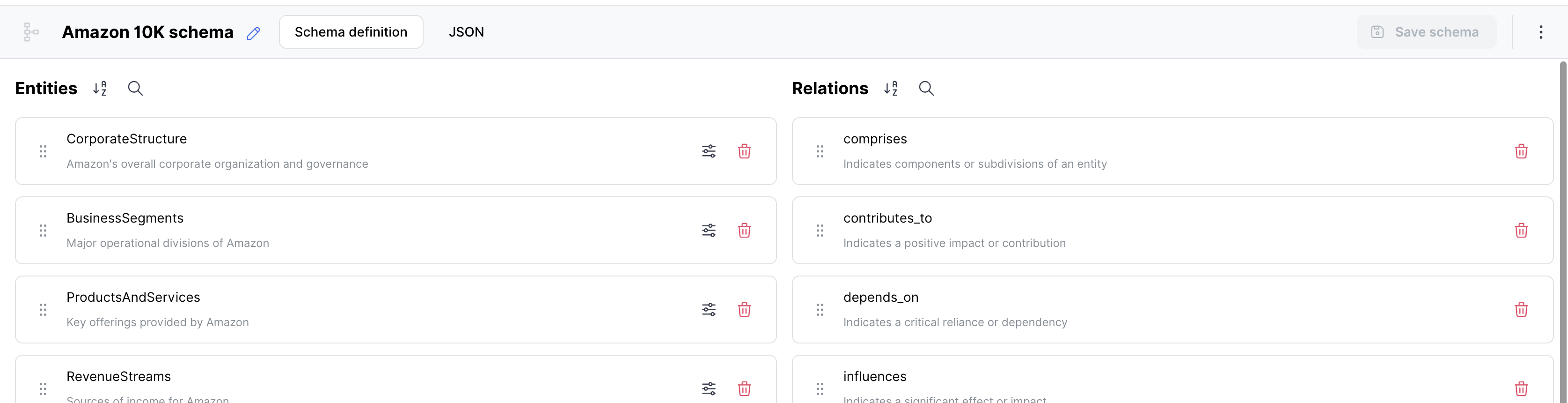
Schema
A schema defines the structure and relationships of the data in a knowledge graph. It specifies the types of entities, their properties, and the relationships between them. Schemas are created using a JSON-like format and serve as a blueprint for generating the knowledge graph.
Entity
Entities are the basic building blocks of a knowledge graph. They represent real-world objects, concepts, or abstractions relevant to the modelled domain. Entities have properties and can be connected to other entities through relationships.
Relationship
Relationships represent the connections or associations between entities in a knowledge graph. They define how entities are related to each other and provide meaning and context to the graph structure. Relationships can have types and properties to capture specific details about the connection.
Triple
Triples are the fundamental units of a knowledge graph. They consist of:
- A subject (an entity)
- A predicate (a relationship)
- An object (another entity or a literal value)
Triples express facts or statements about the relationships between entities in the graph.
Graph
A graph visually represents a knowledge graph, displaying entities as nodes and relationships as edges. It provides an intuitive way to explore and understand the connections and patterns within the data. Whyhow offers interactive graph visualization and querying capabilities.
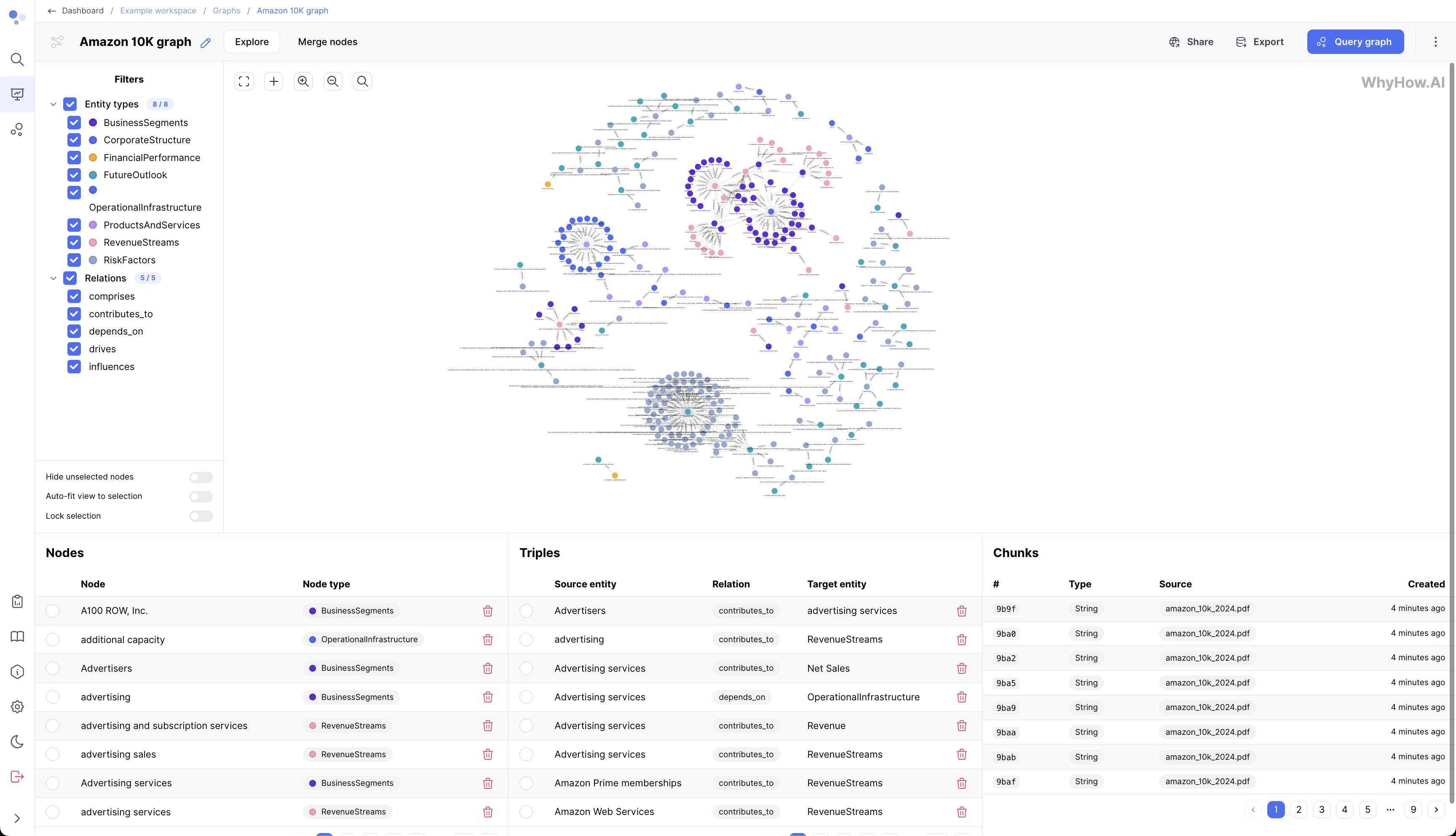
Node
Nodes are the visual representations of entities in a graph. They are depicted as circles or other shapes and can have labels and properties associated with them. Nodes are connected by edges to form the structure of the knowledge graph.
These concepts work together to enable the creation, management, and exploration of knowledge graphs in whyhow. By understanding their roles and relationships, you can effectively model your data, generate insights, and leverage the power of knowledge graphs.
To dive deeper into each concept and learn how to apply them in practice, refer to the individual concept guides in the documentation: